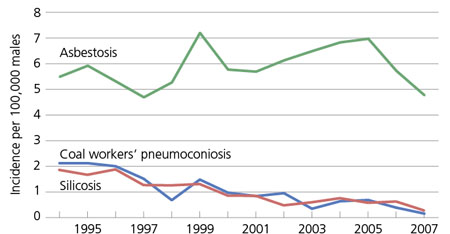
Incidence of asbestosis, coal workers’ pneumoconiosis, and silicosis
per 100,000 men, BC, 1994-2007
In brief
- Asbestosis, silicosis, and coal workers’ pneumoconiosis are fibrotic lung diseases typically associated with exposure to high levels of respirable dust exposure.
- We used outpatient, hospital, and compensation data to examine geographic and time trends for incidence of these pneumoconioses in BC.
- We found that between 1992 and 2006, asbestosis incidence among men increased from 5.5 to 6.2/100,000, and silicosis and coal workers’ pneumoconiosis decreased from 2.3 to 0.3/100,000 and 2 to 0.4/100,000, respectively. Similar trends were observed among women, based on small numbers.
- Incidence of all three diseases varied widely (up to twenty-fold) across BC regions, and showed association with known sites of historic exposure.